Publications
Here you can find my publications, sorted in reverse chronological order, showcasing my contributions to AI, IoT, and blockchain research.
2023
- IEEE TCSS
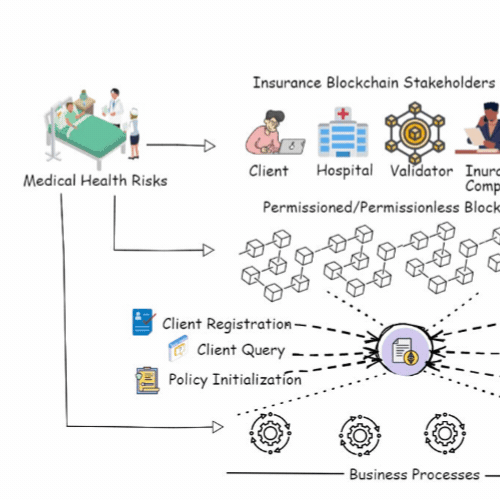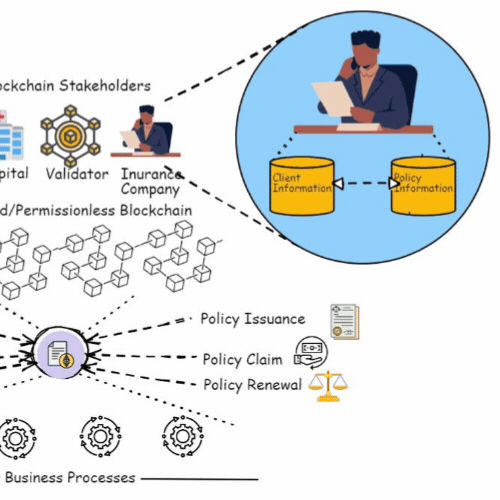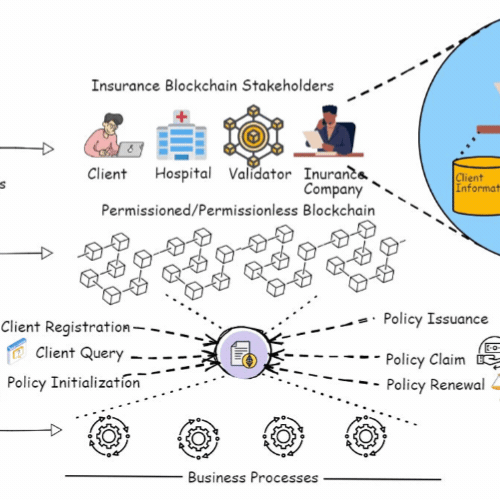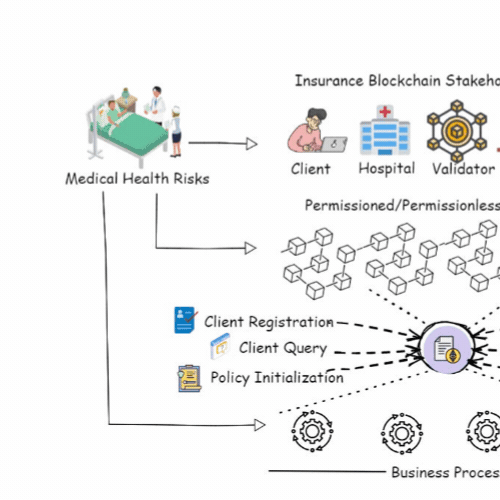 A Blockchain and ML-Based Framework for Fast and Cost-Effective Health Insurance Industry OperationsAnubhav Elhence, Adit Goyal, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, Aug 2023
A Blockchain and ML-Based Framework for Fast and Cost-Effective Health Insurance Industry OperationsAnubhav Elhence, Adit Goyal, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, Aug 2023Health insurance is crucial for each person, bearing in mind the increasing medical costs. COVID-19 has been an eye-opener as to how important it is to have health insurance. Medical emergencies can have a severe emotional and financial impact. Thus, a health insurance policy can help mitigate financial risks in unpredictable circumstances. However, the current insurance system is very expensive, as thousands of people pay the premiums, and very few take the claims. Furthermore, the claim settlement process is excruciatingly long and tiresome. In this article, we focus on establishing a rapid and cost-effective framework for the health insurance market, based on machine learning and blockchain technology. By developing a smart contract, blockchain may eliminate any third-party organizations and make the complete process safer, easier, and more efficient. The contract pays the claim based on the claimant’s documentation. We optimized the premiums using a regression model based on the net amount claimed during the current policy tenure and various other criteria. For anticipating risk, a random forest classifier is used, which aids in the risk-rated premium rebate computation for policyholders for their next term of insurance.
@article{9945906, author = {Elhence, Anubhav and Goyal, Adit and Chamola, Vinay and Sikdar, Biplab}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems}, title = {A Blockchain and ML-Based Framework for Fast and Cost-Effective Health Insurance Industry Operations}, year = {2023}, volume = {10}, number = {4}, pages = {1642-1653}, keywords = {Insurance;Blockchains;Smart contracts;Hospitals;Industries;Medical services;Costs;Blockchain;Ethereum;insurance;machine learning;random forest;regression;smart contract}, doi = {10.1109/TCSS.2022.3219256}, issn = {2329-924X}, month = aug, }
2022
- IEEE IoT Mag
 Enabling Cost-Effective and Secure Minor Medical Teleconsultation Using Artificial Intelligence and BlockchainAnubhav Elhence, Varun Kohli, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, Mar 2022
Enabling Cost-Effective and Secure Minor Medical Teleconsultation Using Artificial Intelligence and BlockchainAnubhav Elhence, Varun Kohli, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Internet of Things Magazine, Mar 2022While the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the popularity of home-based consultations, worries over privacy, high consultations costs, slow response times, and the burden on doctors due to the overwhelming number of COVID-19 cases have made current in-person and online models ineffective. In this study, we present an advanced, privacy-protected, artificial intelligence and blockchain-based consultation framework for minor medical conditions. Patients can post their medical queries anonymously on the blockchain network, which may be answered by any available medical professionals. The queries are sorted into their respective domains using naive Bayes and logistic regression. The consultations provided by medical specialists are evaluated based on their reputation, expertise, detail orientation, and the use of supporting documents, and rewards are given in accordance with the evaluation scheme. This fair and incentivized system provides cheaper and more accessible healthcare to patients, which is the need of the hour.
@article{9773136, author = {Elhence, Anubhav and Kohli, Varun and Chamola, Vinay and Sikdar, Biplab}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Magazine}, title = {Enabling Cost-Effective and Secure Minor Medical Teleconsultation Using Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain}, year = {2022}, volume = {5}, number = {1}, pages = {80-84}, keywords = {COVID-19;Privacy;Medical conditions;Costs;Pandemics;Machine learning;Blockchains;Logistics;Telemedicine;Artificial intelligence;Medical services}, doi = {10.1109/IOTM.001.2100142}, issn = {2576-3199}, month = mar, }
2021
- Science Direct
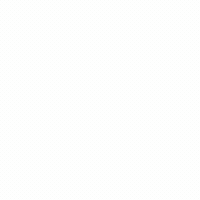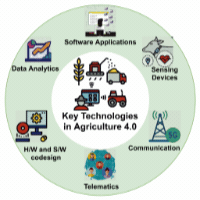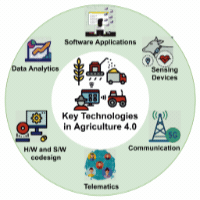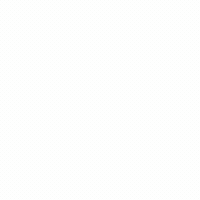 A survey on the role of Internet of Things for adopting and promoting Agriculture 4.0Meghna Raj, Shashank Gupta, Anubhav Elhence , and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, Mar 2021
A survey on the role of Internet of Things for adopting and promoting Agriculture 4.0Meghna Raj, Shashank Gupta, Anubhav Elhence , and 4 more authorsJournal of Network and Computer Applications, Mar 2021There is a rapid increase in the adoption of emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), Internet of Underground Things (IoUT), Data analytics in the agriculture domain to meet the increased food demand to cater to the increasing population. Agriculture 4.0 is set to revolutionize agriculture productivity by using Precision Agriculture (PA), IoT, UAVs, IoUT, and other technologies to increase agriculture produce for growing demographics while addressing various farm-related issues. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of how multiple technologies such as IoT, UAVs, IoUT, Big Data Analytics, Deep Learning Techniques, and Machine Learning methods can be used to manage various farm-related operations. For each of these technologies, a detailed review is done on how the technology is being used in Agriculture 4.0. These discussions include an overview of relevant technologies, their use cases, existing case studies, and research works that demonstrate the use of these technologies in Agriculture 4.0. This paper also highlights the various future research gaps in the adoption of these technologies in Agriculture 4.0.
@article{RAJ2021103107, title = {A survey on the role of Internet of Things for adopting and promoting Agriculture 4.0}, journal = {Journal of Network and Computer Applications}, volume = {187}, pages = {103107}, year = {2021}, issn = {1084-8045}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2021.103107}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1084804521001284}, author = {Raj, Meghna and Gupta, Shashank and Elhence, Anubhav and Chamola, Vinay and Garg, Tanya and Atiquzzaman, Mohammed and Niyato, Dusit}, } - IEEE TIA
 Machine Learning on FPGA for Robust \rm Si_3\rm N_4-Gate ISFET pH Sensor in Industrial IoT ApplicationsSoumendu Sinha, Nishad Sahu, Rishabh Bhardwaj , and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Nov 2021
Machine Learning on FPGA for Robust \rm Si_3\rm N_4-Gate ISFET pH Sensor in Industrial IoT ApplicationsSoumendu Sinha, Nishad Sahu, Rishabh Bhardwaj , and 5 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Nov 2021This article presents performance enhancement of \rm Si_3\rm N_4-gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistor based pH sensor using machine learning (ML) techniques. A robust SPICE macromodel is developed using experimental data, which incorporates intrinsic temperature and temporal characteristics of the device, which is further used in sensor readout circuit (ROIC), which shows a nonideal temperature and time dependence in the voltage output. To make the device robust to the critical drifts, we exploit six state-of-the-art ML models, which are trained using the data generated from ROIC for a wide range of pH, temperature, and temporal conditions. Thorough comparison between ML models shows random forest outperforms other models for drift compensation task. This work also shows a preliminary time series classification task. The ML models are implemented on a Xilinx PYNQ-Z1 field-programmable gate array (FPGA) board to validate the performance in power and memory-restricted environment, crucial for IoT applications. A parameter, implementation factor is defined to evaluate best ML model for IoT deployment using FPGA/MCU hardware implementation. The significantly lower power consumption of FPGA board as compared to CPU with no noticeable performance drop is a pointer to the future of robust pH sensors used in industrial and remote IoT applications.
@article{9556621, author = {Sinha, Soumendu and Sahu, Nishad and Bhardwaj, Rishabh and Mehta, Aditya and Ahuja, Hitesh and Srivastava, Satyam and Elhence, Anubhav and Chamola, Vinay}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications}, title = {Machine Learning on FPGA for Robust ${\rm {Si}}_{3}{\rm {N}}_{4}$-Gate ISFET pH Sensor in Industrial IoT Applications}, year = {2021}, volume = {57}, number = {6}, pages = {6700-6712}, keywords = {SPICE;Sensors;Temperature sensors;Logic gates;Task analysis;Monitoring;Silicon;Drift compensation;field-programmable gate array (FPGA);ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (ISFET);IIoT;IoT;machine learning (ML);MCU;neural networks;pH sensor;random forest (RF);SPICE macromodel}, doi = {10.1109/TIA.2021.3117233}, issn = {1939-9367}, month = nov, } - Sensys 21’
 A Blockchain and Machine Learning based Framework for Efficient Health Insurance ManagementAdit Goyal, Anubhav Elhence, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems , Coimbra, Portugal, Nov 2021
A Blockchain and Machine Learning based Framework for Efficient Health Insurance ManagementAdit Goyal, Anubhav Elhence, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems , Coimbra, Portugal, Nov 2021Having a health insurance is important for everybody, bearing in mind the increasing medical costs. Medical emergencies can have a severe financial and emotional impact. However, the current insurance system is very expensive and the claim settlement process is excessively lengthy, making it tedious. This results in policyholders not being able to successfully make a claim with their insurance company. In this paper, we focus on developing a fast and cost-effective framework based on blockchain technology and machine learning for the health insurance industry. Blockchain is capable of removing all third-party organisations by forming a smart contract, making the entire process more smooth, secure, and efficient. The contract settles the claim on documents submitted by the claimant. A ridge regression model is used for computing the premiums optimally, based on the total amount claimed under the current policy tenure, along with several other factors. A random forest classifier is applied for predicting the risk that helps in the computation of risk-rated premium rebate.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3485730.3493685, author = {Goyal, Adit and Elhence, Anubhav and Chamola, Vinay and Sikdar, Biplab}, title = {A Blockchain and Machine Learning based Framework for Efficient Health Insurance Management}, year = {2021}, isbn = {9781450390972}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3485730.3493685}, doi = {10.1145/3485730.3493685}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems}, pages = {511–515}, numpages = {5}, keywords = {Blockchain, Insurance, Machine Learning, Random Forest, Smart contract}, location = {Coimbra, Portugal}, series = {SenSys '21}, }
2020
- IEEE Access
 Electromagnetic Radiation Due to Cellular, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Technologies: How Safe Are We?Naren, Anubhav Elhence, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Access, 2020
Electromagnetic Radiation Due to Cellular, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Technologies: How Safe Are We?Naren, Anubhav Elhence, Vinay Chamola , and 1 more authorIEEE Access, 2020d
@article{9016183, author = {Naren and Elhence, Anubhav and Chamola, Vinay and Guizani, Mohsen}, journal = {IEEE Access}, title = {Electromagnetic Radiation Due to Cellular, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Technologies: How Safe Are We?}, year = {2020}, volume = {8}, number = {}, pages = {42980-43000}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2976434}, issn = {2169-3536}, month = {}, }